Fossil fuels harm the environment in multiple ways. Their combustion releases pollutants that cause air pollution, smog, and acid rain. These emissions drive climate change, leading to global warming and extreme weather events. Extraction processes destroy habitats and contaminate water sources. Fossil fuel pollution contributes to millions of premature deaths annually worldwide. The economic costs include healthcare expenses and environmental cleanup. The following sections explore these environmental impacts in greater detail.
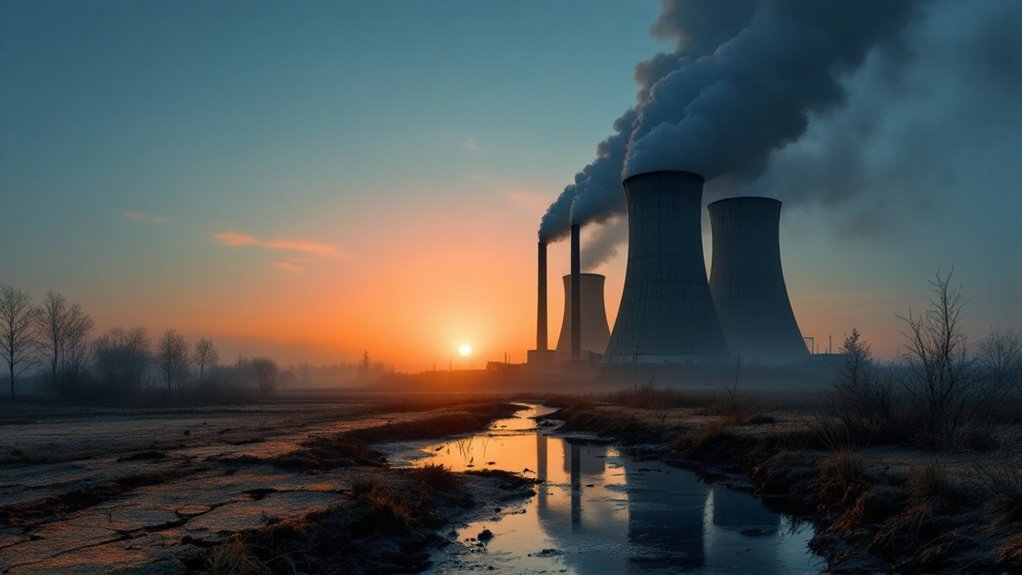

While fossil fuels have powered global development for over a century, they’ve also caused widespread environmental damage. When burned, these fuels release harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter into the air. These chemicals create smog in cities and cause acid rain that damages buildings, forests, and water bodies. They also contaminate water sources through extraction processes and accidental spills.
Fossil fuels are the main driver of climate change. When we burn coal, oil, and natural gas, they release greenhouse gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. According to the IPCC, fossil fuel emissions are the dominant cause of global warming we’re experiencing today. This leads to global warming and more frequent extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and droughts. Methane leaks from natural gas operations also contribute greatly to global warming, as methane is more potent than carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas. The scientific community agrees that human activities are the primary cause of the rapid warming observed in the last century.
Fossil fuels release greenhouse gases when burned, directly driving climate change and increasing extreme weather events globally.
The health effects of fossil fuels are severe. Air pollution from burning these fuels is linked to respiratory problems, heart disease, and strokes. According to research, air pollution causes about 8 million premature deaths worldwide each year. Recent studies suggest that air pollution contributes to approximately 1 in 10 American deaths annually. People living near fossil fuel operations often face higher risks of cancer and developmental issues due to toxic chemicals that enter water supplies.
Ecosystems suffer greatly from fossil fuel activities. Mining, drilling, and building pipelines destroy natural habitats. Oil spills can devastate marine and coastal environments for decades. The acid rain produced by fossil fuel emissions damages forests and kills aquatic life in lakes and rivers. These activities fragment landscapes and reduce biodiversity.
The economic costs are substantial but often hidden. Society pays for healthcare for pollution-related illnesses, environmental cleanup after spills, and climate change adaptation measures. These “external costs” aren’t included in the price of fossil fuels but are paid by communities and governments.
As non-renewable resources, fossil fuels are being depleted while extraction becomes increasingly difficult and environmentally harmful. Compared to renewable energy sources, they’re also less efficient, with considerable energy lost during extraction, processing, and transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Will Remaining Fossil Fuel Reserves Last?
Current fossil fuel reserves are projected to last several decades at today’s consumption rates.
Oil may run out by 2052, natural gas by 2060, and coal by 2090.
However, these timelines aren’t fixed. New discoveries, improved technology, and changing demand all affect how long supplies will last.
Many experts believe economic and environmental factors will limit fossil fuel use before physical depletion occurs.
Can Fossil Fuels Be Made Environmentally Friendly?
Fossil fuels can’t be made completely environmentally friendly, but their impact can be reduced.
Technologies like carbon capture and storage can trap up to 90% of emissions. Companies are developing cleaner extraction methods and blending fossil fuels with renewables.
Efficiency improvements in power plants and vehicles also help. These solutions are promising but costly, and many remain in early development stages.
Who Are the Largest Consumers of Fossil Fuels Globally?
China leads the world in fossil fuel consumption, using 140 exajoules in 2023.
The United States follows in second place with 76 exajoules.
India ranks third with 35 exajoules, while Russia comes in fourth with 27 exajoules.
Japan rounds out the top five, consuming 15 exajoules.
Together, these five nations account for the majority of global fossil fuel use.
How Do Fossil Fuel Subsidies Impact Renewable Energy Adoption?
Fossil fuel subsidies create an uneven playing field for renewable energy.
These subsidies make oil, gas, and coal artificially cheaper, making it harder for solar and wind power to compete.
In 2013, governments spent $548 billion on fossil fuel subsidies but only $121 billion on renewables.
This price distortion slows clean energy investments and reinforces existing fossil fuel infrastructure, hindering the shift to renewable energy sources.
What Careers Are at Risk From Fossil Fuel Phase-Outs?
The shift away from fossil fuels puts several career fields at risk.
Coal miners, now numbering 50,000 in the U.S., have already seen steep job declines.
Oil and gas extraction workers, about 700,000 jobs, face uncertainty by 2050.
Power plant operators, refinery workers, pipeline crews, and fuel transporters will see fewer opportunities.
Even indirect jobs in manufacturing, office work, and local businesses in fossil fuel communities are threatened, affecting an estimated 1.7 million U.S. workers total.