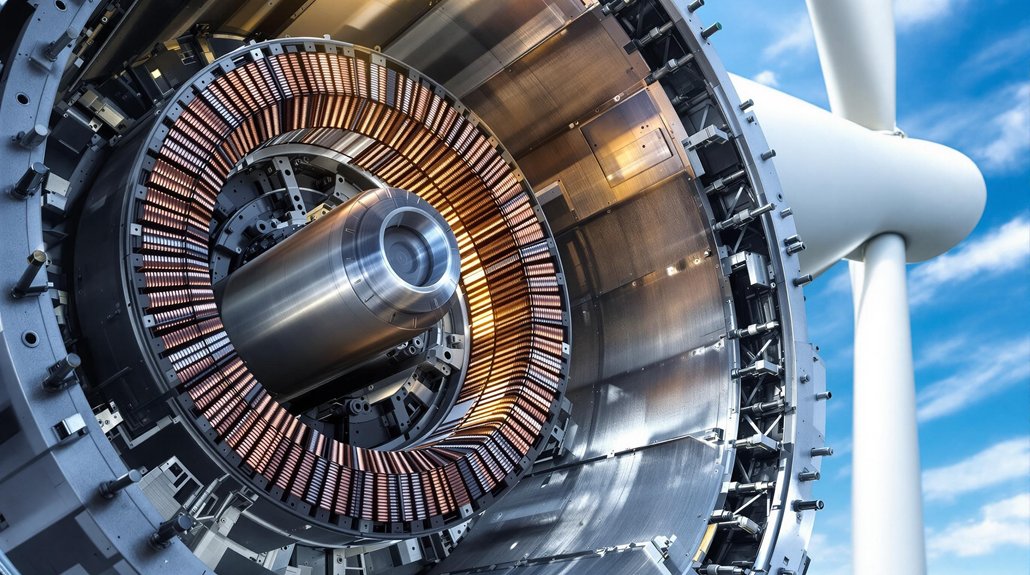
A wind turbine generator converts rotational motion into electricity through electromagnetic induction. When wind spins the turbine blades, the rotor turns inside the stationary stator. The rotor’s magnetic field passes through copper coils in the stator, creating an electric current. Different generator types exist, including induction and permanent magnet models. Wind speed greatly affects power output—doubling wind speed increases power eightfold. The electricity is then conditioned to meet grid standards before distribution.

Every wind turbine across the world relies on a critical component to transform the power of moving air into usable electricity: the generator. This device operates on a principle called electromagnetic induction, first discovered by scientist Michael Faraday. When wind causes the turbine blades to spin, this rotational energy travels down the shaft to the generator where the magic happens.
Inside the generator, there are two main parts: the rotor and the stator. The rotor contains magnets or electromagnets and spins with the turbine shaft. The stator remains stationary and contains coils of copper wire wrapped around an iron core. As the rotor spins inside the stator, its magnetic field passes through the copper coils. This movement of magnetic field across the conductors creates an electric current in the wires.
Magnetic motion becomes electricity as the spinning rotor’s field cuts through the stator’s copper coils.
Different types of generators are used in wind turbines. Synchronous generators, induction generators, and permanent magnet generators are common choices. Modern wind farms often employ doubly-fed induction generators (DFIG) or direct drive systems, depending on the turbine design and specific needs. The entire system works efficiently only when the yaw system properly aligns the turbine with the wind direction to maximize energy capture.
The amount of electricity produced depends on several factors. Wind speed has a cubic relationship with power output—when wind speed doubles, the power increases eight times. The powerful relationship between wind velocity and energy output is precisely expressed by the formula P = 1/2 ρ A V^3. The generator’s size, rotor diameter, and overall turbine design also affect how much electricity is produced. Most wind turbine generators operate at impressive efficiency levels between 90 to 97 percent.
Before the electricity can be sent to homes and businesses, it must be properly conditioned for the power grid. Power electronics handle voltage and frequency regulation, ensuring the electricity meets grid standards. These systems also manage reactive power and help turbines ride through grid faults without disconnecting.
Cooling systems prevent the generator from overheating during operation. As the copper windings carry current, they generate heat through resistance. Proper cooling extends the generator’s life and maintains efficiency, allowing wind turbines to provide clean, renewable energy for many years.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does a Typical Wind Turbine Generator Last?
A typical wind turbine generator lasts 20-25 years before needing replacement. Some units can operate up to 30 years with proper maintenance.
Lifespans vary based on environmental conditions, with offshore turbines often having shorter lives due to harsh saltwater exposure. Regular inspections every 6-12 months help extend longevity.
Replacement costs range from $100,000 to $500,000, though newer models offer improved efficiency to offset these expenses.
Can Wind Turbine Generators Operate in Extreme Temperatures?
Wind turbine generators can operate in extreme temperatures with proper equipment. They function in cold weather down to -22°F, and with special packages, as low as -40°F.
In hot regions, they work at temperatures up to 104°F, with some models handling 122°F. Temperature sensors monitor key components, and control systems adjust operation accordingly.
Special cooling systems prevent overheating, while heating systems prevent freezing in cold conditions.
What Maintenance Does a Wind Turbine Generator Require?
Wind turbine generators need regular upkeep to run efficiently.
Technicians inspect windings and insulation twice a year and tighten electrical connections annually. They analyze oil samples every 3-6 months to spot early wear. Vibration monitoring helps detect bearing problems before they cause failures.
The cooling system needs yearly cleaning, while thermographic scans identify potential hot spots.
Complete generator rewinding occurs every 7-10 years, depending on the unit’s condition.
How Efficient Are Modern Wind Turbine Generators?
Modern wind turbine generators are highly efficient. They typically reach 95-98% efficiency in converting mechanical energy to electricity.
Permanent magnet generators achieve the highest rates. Direct drive systems eliminate gearbox losses, further improving performance. Efficiency increases with turbine size.
While generators are efficient, the overall wind turbine system captures only 35-45% of wind energy due to physical limitations and the Betz limit of 59.3%.
Can Wind Turbine Generators Store Excess Electricity?
Wind turbine generators don’t store electricity themselves. They convert wind’s motion into electrical power that flows directly to the grid.
For storage, separate systems are needed. These include batteries, pumped hydro, compressed air, hydrogen, or flywheels.
Storage helps manage wind’s variability, prevents energy waste during high winds, and guarantees power is available when needed.
Storage costs remain high but are falling as technology improves.