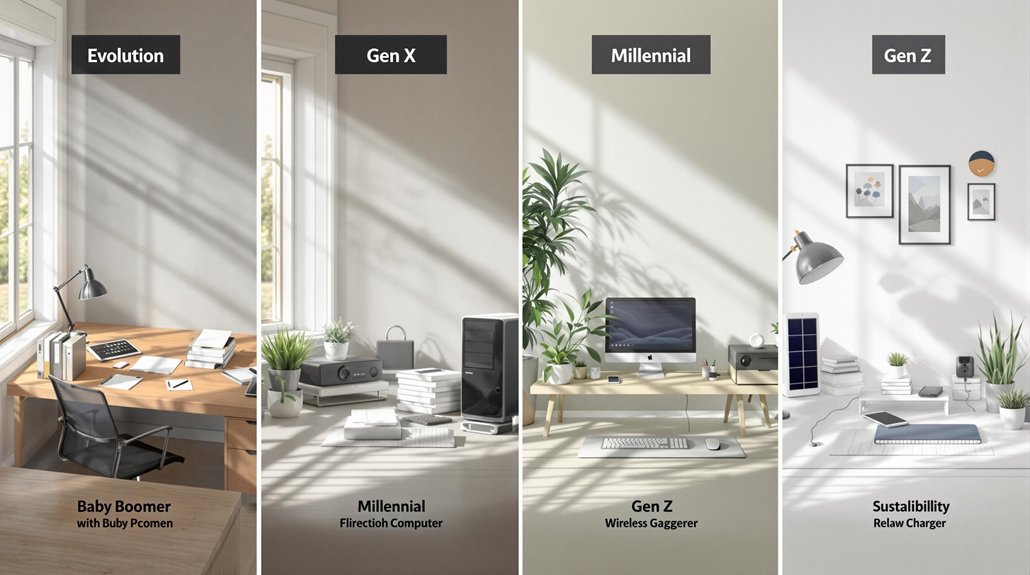
Generational traits vary widely across age groups. Baby Boomers (1946-1964) value career stability and face-to-face communication. Gen X (1965-1980) prizes independence and work-life balance. Millennials (1981-1996) seek purpose in work and embrace technology. Gen Z (1997-2012) expects digital integration and prioritizes flexibility, diversity, and social justice. These patterns, shaped by shared experiences, impact approaches to work, money, and society. These differences influence workplace dynamics in significant ways.

While everyone is unique, the generation someone belongs to often shapes their values, work habits, and worldview. Today’s workforce includes four distinct generations, each with characteristics formed by the events and culture of their formative years.
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, find much of their identity in their careers. They’re known for being hardworking, competitive, and goal-oriented. They value job security and financial stability. Boomers currently control over half of America’s wealth. Many are entering retirement at a rate of 11,200 per day between 2024 and 2027. They prefer face-to-face meetings and tend to hold more conservative views and religious beliefs.
Generation X, born from 1965 to 1980, grew up as latchkey kids, making them independent and self-reliant. They were the first generation to use computers regularly. Gen Xers value work-life balance more than Boomers do. They’re adaptable and resourceful in the workplace. Many face financial pressure as they care for both children and aging parents.
Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, are tech-savvy digital natives. They seek purpose in their work and value experiences over possessions. Millennials prefer collaborative work environments and flexible schedules. Financial challenges have caused many to delay buying homes or starting families. They generally hold more liberal social views and actively support environmental and social causes.
Generation Z, born from 1997 to 2012, has never known a world without smartphones and social media. They’re pragmatic, financially conscious, and entrepreneurial. In the workplace, they expect technology in all aspects of their jobs. Research shows they prefer to job hop more frequently than older generations, prioritizing flexibility and meaningful work over long-term employment. They show early interest in saving money and financial education.
Gen Z is the most diverse generation yet and strongly values inclusion. They share Millennials’ concern for social justice and environmental issues but take an even more active stance.
Understanding these generational differences helps workplaces function better. While these traits don’t apply to everyone, they provide insight into how different age groups approach work, money, and society based on their shared experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Generational Boundaries Affect Workplace Dynamics?
Generational boundaries create noticeable differences in workplace interactions.
Baby Boomers prefer face-to-face meetings while Gen Z relies on digital communication. This can lead to misunderstandings when teams collaborate.
Different generations also have varying expectations about leadership, work-life balance, and technology use. These differences can cause friction, but they’re also bringing diversity of thought to companies.
Many businesses now offer training to help bridge these generational gaps.
Can Individuals Exhibit Traits From Multiple Generations?
Research confirms that individuals commonly exhibit traits from multiple generations. A Pew Research Center study shows 33% of Millennials identify with Gen X traits.
Similar findings from IBM indicate 60% of employees don’t match generational stereotypes. Factors like education, socioeconomic status, and geographic location contribute to this trait fluidity.
Family dynamics, personal experiences, and cultural background also shape values beyond generational boundaries, creating unique combinations of characteristics in each person.
How Do Cultural Differences Impact Generational Traits Globally?
Cultural differences greatly shape generational traits around the world. Economic conditions, technology access, and local values create distinct experiences within the same age groups.
Power distance varies widely, with Baby Boomers showing the lowest levels globally. Digital communication tools bridge some gaps but can’t eliminate fundamental differences.
Immigration patterns further diversify generational characteristics within countries. The wealth gap impacts generations differently across ethnic groups, creating unique challenges in each society.
Are Generational Traits Scientifically Proven or Social Constructs?
Generational traits are largely social constructs rather than scientifically proven facts. Research shows limited empirical evidence for distinct generational characteristics.
Studies face methodological challenges like confusing age effects with generational ones. While shared historical events can influence groups, differences often stem from life stages, socioeconomic factors, and individual experiences.
Scientists caution against overgeneralizing diverse populations based on birth years alone.
How Should Businesses Adapt Marketing for Different Generations?
Businesses are tailoring marketing to reach different age groups effectively.
Baby Boomers respond to traditional media and detailed information. Gen X prefers authentic messaging and email campaigns. Millennials engage with social responsibility and mobile content. Gen Z connects through short videos and interactive experiences.
Companies now analyze these preferences to create targeted campaigns across various platforms. Marketing strategies continue evolving as media habits shift among generations.